The last thing you want when you have worked so hard to create a lovely garden or house is for invasive roots to ruin your hard work. Root barriers made of HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) can be used in this situation. We will go further into the details of HDPE root barriers in this helpful guide, learning what they are, why are they so important and how to utilize them to protect your house’s investment.
You might like: Root Barrier Myths: 5 Misconceptions That Could Hurt Your Home
Working Of HDPE Root Barreiers
HDPE root barriers are the great landscape items made to stop plant roots from spreading into undesirable places like close to foundations, paved areas or utility lines. These barriers serve as a protective tool, forming an impenetrable barrier that diverts roots from delicate structures.
What Are HDPE Root Barriers?
Root barriers for foundation protection are essential in preventing costly damage caused by invasive tree roots. HDPE root barriers are sheets or panels made from high-density polyethylene, a thermoplastic polymer valued for its exceptional strength, resilience, and chemical resistance. Acting as an impenetrable underground wall, these barriers effectively stop roots from encroaching into protected zones such as building foundations, sidewalks, and underground utilities.
Key Properties of HDPE Root Barriers
High Strength – Resistant to root penetration and soil pressure
Flexible Yet Durable – Can be shaped around landscapes without cracking
Weather-Resistant – Performs in both hot and cold climates
Eco-Friendly – Non-toxic and reusable, unlike chemical solutions
Long Lifespan – Typically lasts 50 years or more without degradation
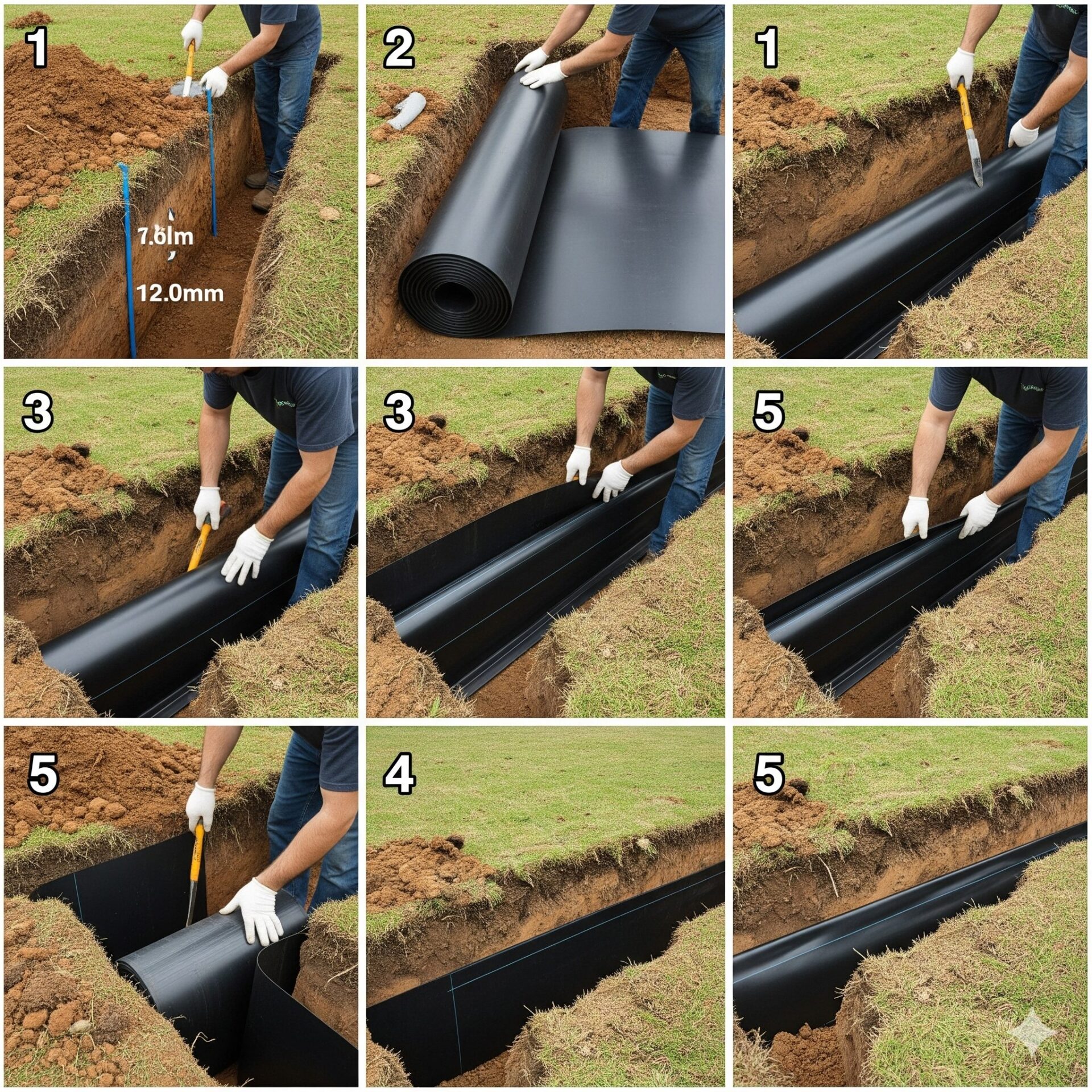
HDPE Root Barrier Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Installing HDPE root barriers correctly is essential to ensure long-term effectiveness. While the material itself is durable, improper installation can reduce its ability to block root intrusion. Below is a step-by-step guide for successful installation.
Step 1: Site Evaluation
Before digging, carefully assess the location. Key considerations include:
Tree Species and Root Behavior – Some trees have aggressive, shallow roots, while others grow deep. Choose the appropriate barrier depth (typically 24-48 inches).
Proximity to Structures – Evaluate how close trees are to foundations, sidewalks, or underground utilities.
Soil Conditions – Loose or sandy soils may require deeper installation and extra compaction, while clay soils provide natural resistance.
Drainage Patterns – Ensure barriers don’t block natural water flow, which could harm tree health or cause pooling near structures.
A thorough site evaluation ensures the barrier is placed strategically to redirect roots without harming the tree.
Step 2: Excavation
Dig a trench along the perimeter of the protected area.
Depth: 24–48 inches, depending on the root system.
Width: Wide enough to accommodate the HDPE sheet with proper backfill.
Step 3: Positioning the HDPE Barrier
Place the HDPE sheets vertically in the trench.
Overlap sheets by at least 12 inches to avoid gaps.
Secure joints with fasteners or adhesive tape designed for HDPE.
Allow 2–3 inches of the barrier to remain above ground to stop surface roots from crossing over.
Step 4: Backfilling and Compaction
Refill the trench with excavated soil.
Compact the soil in layers to prevent air gaps.
Ensure the barrier stays upright and aligned.
Step 5: Inspection and Finishing
Check for exposed gaps or misaligned sheets.
Verify that barrier edges above ground are visible and secure.
Smooth the soil surface for landscaping or pavement.
Installation Methodology
The methodology to install HDPE root barriers is not as easy as it sounds so to make sure you don’t make any fault it is preferred to contact a professional service provider for root barriers installation. However, the method includes the following steps:
- Dig Trenches: Dig trenches along the places where the barriers will be installed.
- The HDPE root barriers should be laid in the trenches so that they are deep enough to prevent root incursion.
- Backfill the trenches and compact the dirt to properly anchor the barriers.
- Test the barriers ability to reroute root growth by watering the soil to settle it.
- Restore the landscape to its former splendor through landscaping.
- Periodic Inspections for Your HDPE Root Barriers
- Check your barriers frequently for any indications of damage or root infiltration. To keep them working, deal with problems right away.
Root barrier installation factors to take into account
When organizing the installation of a Root Barrier, the following must be taken into account:
- Site Evaluation: Based on the soil, slope, and type of vegetation, a specialist will need to assess the site to decide what kind of root barrier is required.
- Excavation: It is required in the vicinity of the structure where the root barrier will be erected.
- Building a trench: To build a trench, this operation will include clearing away vegetation and soil. Temporary ground support may be required for the installation of deep root barriers, along with risk assessment. Root barriers are installed in trenches that are normally dug using an excavator for deep root barriers or by hand or with a specialized soil saw for shallow root barriers.
- Anchoring: To stop barrier material from shifting, horizontal barriers and root barrier cells may need to be anchored. It must be taken into account to anchor the barrier without piercing it.
- Root barrier joining and welding options for bigger installations include site welding, off-site pre-welding, and root barrier joining utilizing barrier tape or glue. Different manufacturers may have different specifications.
- Protection: If the soil profile contains sharp items or there is a risk of penetration, some root barrier manufacturers may specify sand bedding or additional fleece.
- Integration of root barriers into built structures: Where the barrier is to become a crucial component of construction, expert advise on how to install root barriers is required. Root barriers can occasionally be built into foundations, connected to walls, or fastened to buildings.
- Backfilling: After putting in the root barrier, the trench is refilled with dirt and compacted to stop settling. It is usual practice to remove the soil prior to installing a Deep Root Barrier and replace it with an engineering aggregate that is better able to withstand compaction.
Corrections and Repairs
To guarantee that the barriers continue to shield your home, modify them as necessary or make repairs.
Putting money into your home or garden is a labor of love. Consider using HDPE root barriers as your first line of defense against invading roots to safeguard this investment. These barriers guarantee that your landscape will continue to be a source of pride and beauty for years to come thanks to their durability, ease of installation, and long-term advantages. Always remember that prevention is the key to a healthy garden and HDPE root barriers are the ideal answer. Protect your home right away and benefit from the confidence that comes from knowing your investment is safe.

Applications of HDPE Root Barriers
Residential Use
Around driveways, patios, and garden beds
Protecting home foundations
Preventing root invasion into septic tanks or underground irrigation
Commercial Use
Along sidewalks, schools, shopping centers
Protecting parking lots and building perimeters
Controlling root growth in landscape design projects
Municipal and Infrastructure Use
Along roadways and highways
Around underground utilities such as water, sewer, and gas lines
In public parks and urban greening projects
Agricultural Use
Containing root spread in orchards and vineyards
Protecting greenhouse foundations and irrigation systems
Managing invasive plant species in farmland
Case Example: HDPE Barriers in Urban Landscaping
In many cities, sidewalk damage from tree roots is one of the most frequent complaints. Municipalities that switched from concrete or metal barriers to HDPE sheets reported:
Reduced maintenance costs by up to 40%
Increased sidewalk longevity
Improved tree health since roots were redirected instead of severed
This demonstrates how HDPE root barriers serve as a balanced solution that protects infrastructure without sacrificing greenery.
Pros and Cons of HDPE Root Barriers
Pros
Extremely durable and long-lasting
Flexible for different applications
Resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and punctures
Cost-effective in the long run
Environmentally safe
Cons
Requires trench excavation for installation
Initial cost higher than fabric barriers
Not a DIY solution for large projects, professional installation recommended
Conclusion
Tree roots can be both a blessing and a challenge. While they bring life to landscapes, they also pose risks to structures and underground systems. HDPE root barriers offer a modern, eco-friendly, and highly effective solution for managing root growth without harming the environment.
From residential gardens to large-scale municipal projects, HDPE barriers have proven their value in protecting foundations, sidewalks, utilities, and landscapes. Their durability, flexibility, and long-term performance make them the preferred choice over concrete, metal, or chemical alternatives.
Worried about tree roots damaging your home? Protect your investment with HDPE root barriers for foundation protection. Call R.L. NELSON Foundation Solutions at 281-420-1739 today for expert guidance and installation.




